The term "peer-to-peer network" might sound a bit complicated or technical at first glance, but it’s actually simpler and more relatable than it appears. You’ve likely used this type of network countless times without even realizing it. From sharing files online to connecting with friends through messaging apps, peer-to-peer networks have silently become a crucial backbone of modern communication and data sharing.
But what exactly does "peer-to-peer" mean, and how does this system differ from traditional networks? Let’s unpack these questions and explore exactly how peer-to-peer (often shortened to P2P) networks function, why they're popular, and the advantages they bring to everyday digital life.
What Exactly is a Peer-to-Peer Network?
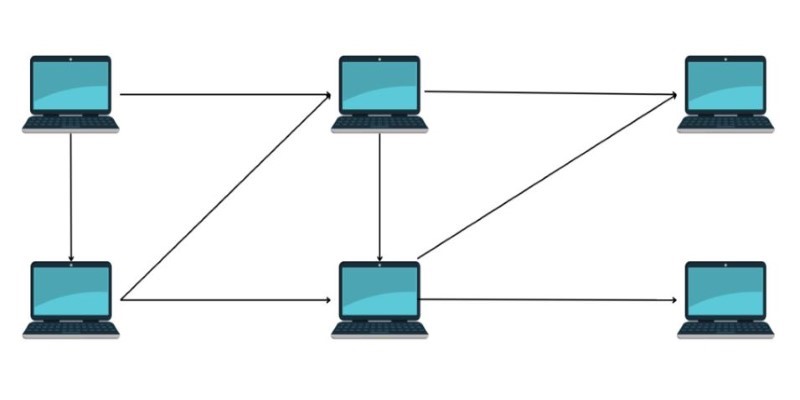
Imagine you're sitting in a room full of friends, passing notes back and forth without a teacher or supervisor controlling the exchange. This informal, straightforward method of passing information is similar to how peer-to-peer networks function. Essentially, a peer-to-peer network links several computers or devices directly to one another. Each device, or peer, can function as both a client and a server. In contrast to conventional systems, there is no central server running or controlling the whole operation.
In traditional client-server models, one central computer holds all the authority and resources. If you request something, the central server answers. However, in a peer-to-peer network, every connected device shares resources directly. This structure creates a decentralized system, making it resilient, robust, and flexible. If one peer leaves the network or fails, the rest of the network can continue without interruption.
Understanding How a Peer-to-Peer Network Functions
Peer-to-peer networking is based on the premise of equality between devices. Every device (peer) is able to send, receive, and save information, so there is no reliance on a central governing computer. If you need a specific item of information, your machine broadcasts a request over the network. Devices that possess the desired information will reply, and you can obtain what you require straight from them.
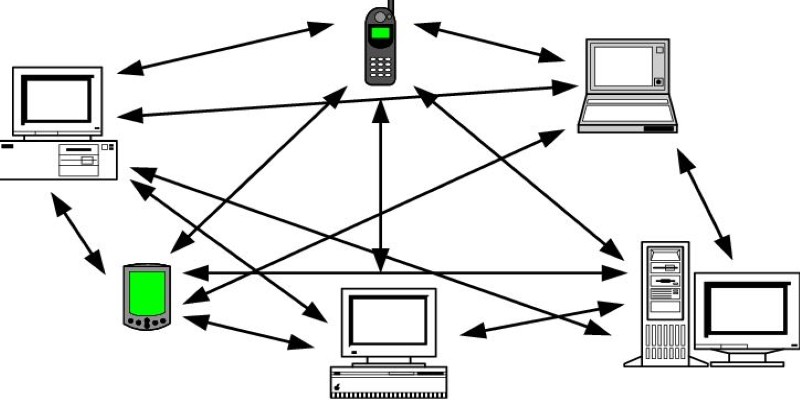
Think of it as borrowing sugar from neighbors. Instead of driving to a supermarket (central server), you simply knock on your neighbor's doors until you find one who can provide it. The network adapts dynamically—neighbors (or devices) come and go, but the community (the network) still functions smoothly. This decentralized approach allows for greater flexibility and reliability.
A practical example of this is file-sharing platforms. Services like BitTorrent are classic instances where large files are split into smaller pieces, each peer holding parts of the file. When downloading, your computer connects directly with multiple peers simultaneously, fetching small chunks from different locations and assembling them efficiently into one coherent file.
Advantages of Using Peer-to-Peer Networks
Peer-to-peer networks offer several benefits that make them a preferred choice for data sharing, communication, and decentralized computing.
Decentralization and Reduced Dependency
One key benefit of peer-to-peer networks is their decentralization, which eliminates reliance on a single control point. Unlike traditional client-server models, which can become bottlenecks during high-traffic periods, P2P networks distribute the load naturally. Each device functions independently, ensuring smoother data transfers and preventing network congestion.
Resilience and Reliability
Peer-to-peer networks are highly resilient because there is no central server that, if compromised, could disrupt the system. If one peer disconnects, the network continues to function through alternative connections. This redundancy enhances stability and ensures uninterrupted data exchange.
Cost Efficiency
Running a traditional server-based network can be costly due to infrastructure, maintenance, and operational expenses. Peer-to-peer networks eliminate these costs by utilizing participants’ devices as both clients and servers. This approach significantly reduces overall expenses, making P2P an affordable alternative for large-scale data sharing.
Enhanced Privacy and Control
With no central authority overseeing data exchange, peer-to-peer networks provide greater privacy. Users control their data, deciding what to share and with whom. This decentralized structure minimizes surveillance risks and enhances security, making it an attractive option for individuals prioritizing data protection and autonomy.
Challenges and Concerns of Peer-to-Peer Networks
Despite their efficiency and flexibility, peer-to-peer networks come with certain drawbacks that can affect security, reliability, and performance.
Security and Trust Issues
Peer-to-peer networks lack a central authority to monitor data exchange, making them vulnerable to malicious users distributing malware or harmful files. Without built-in verification, users must rely on reputation systems or security measures to protect their data. This decentralized model raises trust concerns, requiring caution when sharing or downloading content.
Data Reliability and Network Stability
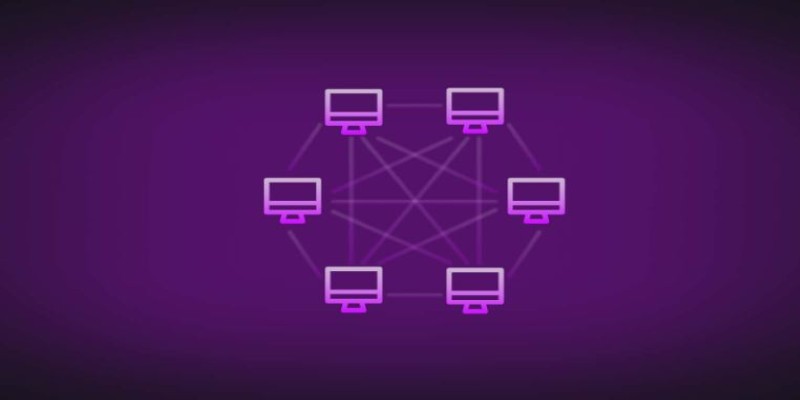
Unlike centralized networks, peer-to-peer networks depend on voluntary participation, leading to inconsistent data availability. If peers frequently disconnect or fail to share resources, the network’s efficiency declines. This unpredictability can disrupt services requiring stable connections, such as streaming or large-scale downloads, making reliability a major concern for P2P users.
Bandwidth Limitations
P2P networks distribute data-sharing responsibilities across multiple devices, often straining individual bandwidth. Since users upload and download simultaneously, internet speed may drop, causing lag and inefficiencies. Those with limited data plans or slow connections may struggle to maintain smooth performance, making bandwidth management a key issue in decentralized networking.
Legal and Ethical Concerns
Peer-to-peer networks are often associated with copyright infringement and illegal file-sharing, leading to legal scrutiny. While the technology has many legitimate uses, such as open-source distribution and research collaboration, its reputation remains controversial. Users must be cautious, ensuring compliance with laws while benefiting from P2P’s decentralized and efficient structure.
Conclusion
Peer-to-peer networks have reshaped how we share, connect, and communicate digitally. Their decentralized nature fosters resilience, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness, making them invaluable in file sharing, cryptocurrencies, gaming, and beyond. While security and reliability challenges persist, the benefits far outweigh the risks. This technology empowers users with direct control over their data and interactions, eliminating dependence on central authorities. As digital landscapes evolve, peer-to-peer networks will continue playing a pivotal role in decentralization and innovation. Understanding how they work helps us navigate the digital world more effectively, appreciating the silent but powerful infrastructure that supports our everyday connectivity.